Mailgun is a robust transactional email relay service and API that lets you send, receive, and track emails via their secure relay servers. Mailgun can integrate with services like postfix (in this tutorial we will learn to configure Mailgun SMTP relay in Postfix), send email using a Mailgun-provided SMTP relay, and integrate with your existing apps.
Mailgun, for example, may distribute emails from a CMS like WordPress when correctly configured.
What is Mailgun?
Mailgun provides API services for sending email, among other things. Sending, receiving, and validating email at scale using your domain. You can also track the performance of your emails by tracking their open, click, bounce, and delivery.
You have the choice of sending your messages via API (A flexible and popular means of sending emails that interfaces with languages such as Python, PHP, Ruby, and more.) or SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, which is an easy way to transfer your emails.)
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is the industry standard for sending and receiving email over the internet.
What is an SMTP relay?
An SMTP relay is a mail server or “MTA” (Message Transfer Agent) that is instructed to pass your message on to another mail server that can deliver it to its intended destination – the finish line.
Get exclusive access to all things tech-savvy, and be the first to receive
the latest updates directly in your inbox.
An SMTP relay service is just an SMTP relay that is hosted “in the cloud” rather than on your own server. The service accepts a message from your server, queues it for delivery to its eventual destination, and then either delivers the message successfully or generates a “NDR” (Non-Delivery Report) or “bounce” that is sent back to the original sender with details on why it was not delivered.
How SMTP relay works?
Before sending the message, email servers with SMTP enabled perform a few more procedures. A virtual envelope is created by the server for each recipient address. It also takes care of adding headers to the message, which can be used to identify the message’s various attributes.
With SMTP and related relay services, authentication is frequently employed. Authentication prevents spammers from accessing company servers for junk mail because SMTP servers are open to the public and run on the Internet. To stop spammers, ISPs and other email providers, such as Gmail, use verification on public relay servers.
SMTP handles delivering messages over the Internet, but what if you need to send a large number of emails for your company? Mass email is used by many firms to send marketing messages, notifications to a large number of users, and for a variety of other purposes. Businesses can utilize their email servers to send mass email using an SMTP relay service, which takes care of the opt-out and unsubscribe restrictions. Without relay services, the company’s domain or internal email servers may be blacklisted as spam.
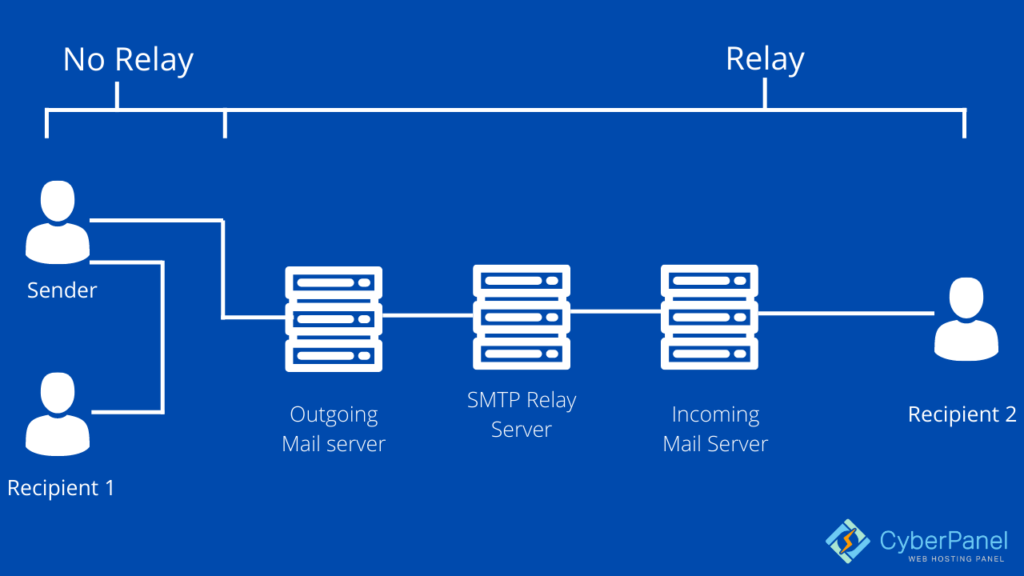
You couldn’t send email messages to someone outside your domain without SMTP, which is obviously an issue because, more than likely, your company uses transactional and mass emails to communicate with subscribers and customers on a daily basis.
Your email software or client establishes an SMTP connection when you click’send’ on your email message. Your server (also known as the sending mail server or SMTP client) connects to the SMTP server of your receiver. At each phase of the sending process, they use a variety of SMTP instructions, or short words, to transport data and enable authentication.
Your email address, the recipient’s email address, and the body of your message are all sent over the SMTP client. Your emails will be sent if everything checks okay.
Advantages of SMTP Relay
Three primary elements have an impact on your capacity to send email successfully:
- Your email infrastructure using SMTP
- Reputation of the sender
- The information in your messages.
Businesses utilize SMTP relay services to improve email deliverability while avoiding technical issues that could jeopardize their capacity to send.
Five benefits of SMTP relay services:

- Your sending infrastructure is transformed by SMTP relay providers.
Your domain and IP address reputation are used by Internet service providers (ISPs) to determine whether your emails are routed to your recipients’ inboxes or sent straight to the spam folder.
A good SMTP relay service provider adds your firm to a list of reliable, high-reputation senders and uses a range of techniques to protect your IP reputation.
You can’t control the reputation of your sending IP if you maintain your own SMTP server on a shared Virtual Machine (VM), which means you could be sharing it with someone sending unwelcome mail. Your IP address may be blacklisted as a result of this, forcing you to work your way back into your ISP’s good graces.
- SMTP relays allow companies to transmit massive amounts of email.
To deter spammers and criminal actors, several ISPs and webmail providers impose email transmission limits. Because these services are designed for user mail rather than application email, such as order confirmations, this is the case. This might limit your company’s capacity to nurture, engage, and assist its customer base unnecessarily, especially if you send a lot of emails.
- SMTP relay providers provide experienced technical assistance.
Who wouldn’t want to collaborate with the very best? Providers of SMTP relay services specialize in delivering, monitoring, and improving email sending operations. You’ll have access to a high-quality email infrastructure as well as an experienced, on-call support team to assist you with any email difficulties or deliverability issues.
- SMTP relay services alert you to concerns with deliverability and provide statistical insights.
Clients who transfer out of their own server to Postmark’s SMTP relay service frequently tell us that they previously couldn’t get a clear understanding of their deliverability. For example, they had no way of knowing how many of their emails were bouncing or why.
Deliverability data, such as emails sent, bounces (and the sort of bounce), spam notices, spam accusations, descriptive error codes, and more, is collected by SMTP relay services.
In other words, SMTP services provide value beyond the ability to hit “send”: they provide essential data and insights, so you’ll know why your email arrives smoothly or fails to arrive.
- SMTP relay providers include user-friendly interfaces that save time.
Apart from a self-managed server, several SMTP relay services ship with a simple, beautiful user interface (UI). Anyone in your organization can easily locate, surface, and interpret email information with an improved user interface. It also reduces back-and-forth emails and tedious searches for email information.
How to setup a Mailgun SMTP relay?
Adding and verifying domain in Mailgun
- Go to your Mailgun Dashboard
- Click Sending -> Domains from the left hand side menu
- Click on “New Domain”
- Enter your domain name and click “Add Domain”
- Your domain is added
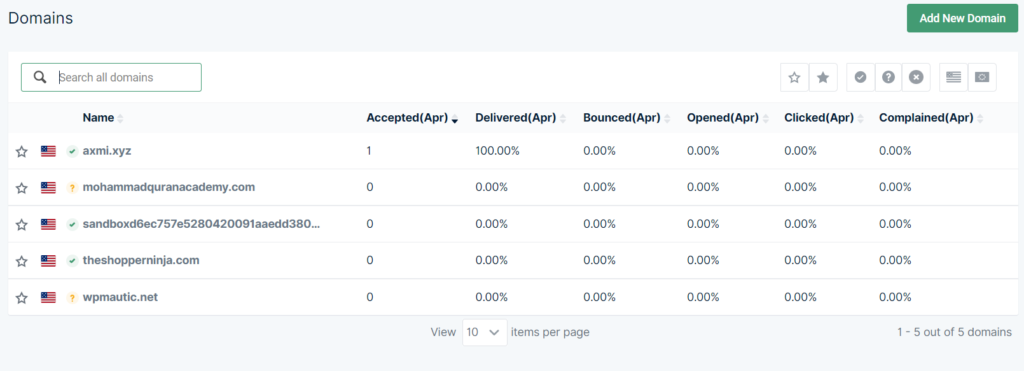
- Now click on sending -> Domain setting from the left hand side menu. Select your domain and click on DNS records
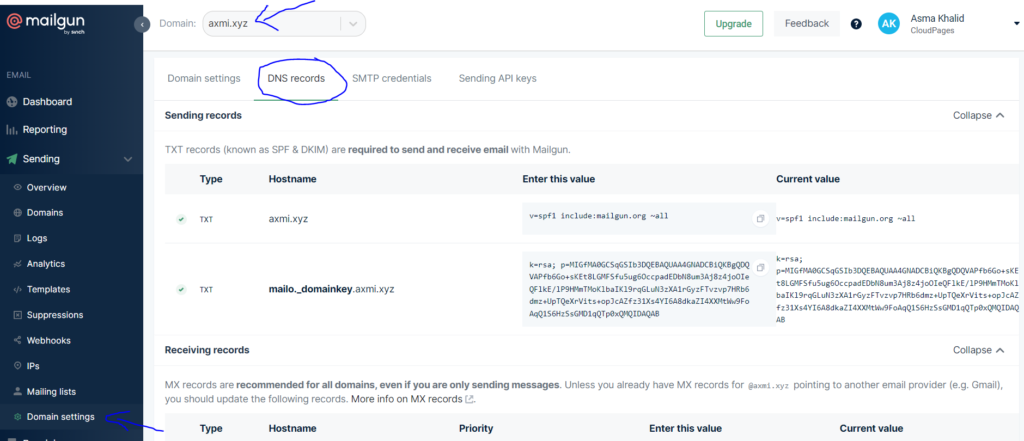
- Enter these TXT and CNAME records in your DNS manager (Cloudflare), to verify your domain
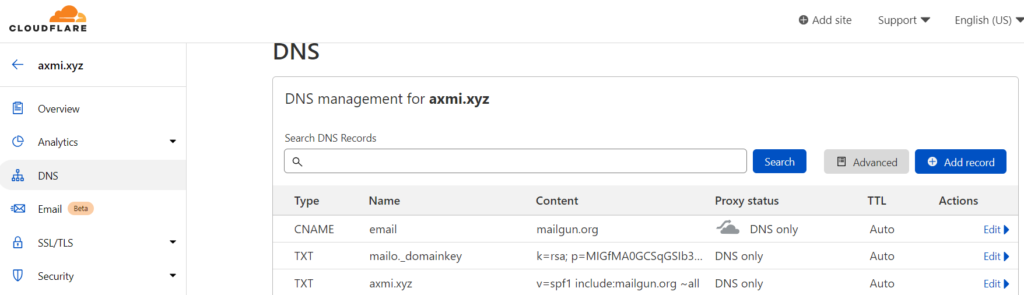
- Click on “Verify Domain” (In Mailgun, after entering records in Cloudflare)

- Your domain is verified.
Create website and Issue Mailserver SSL in CyberPanel
Note: This step is only required if Mailserver SSL is not issued previously, if it is, you can skip this step.
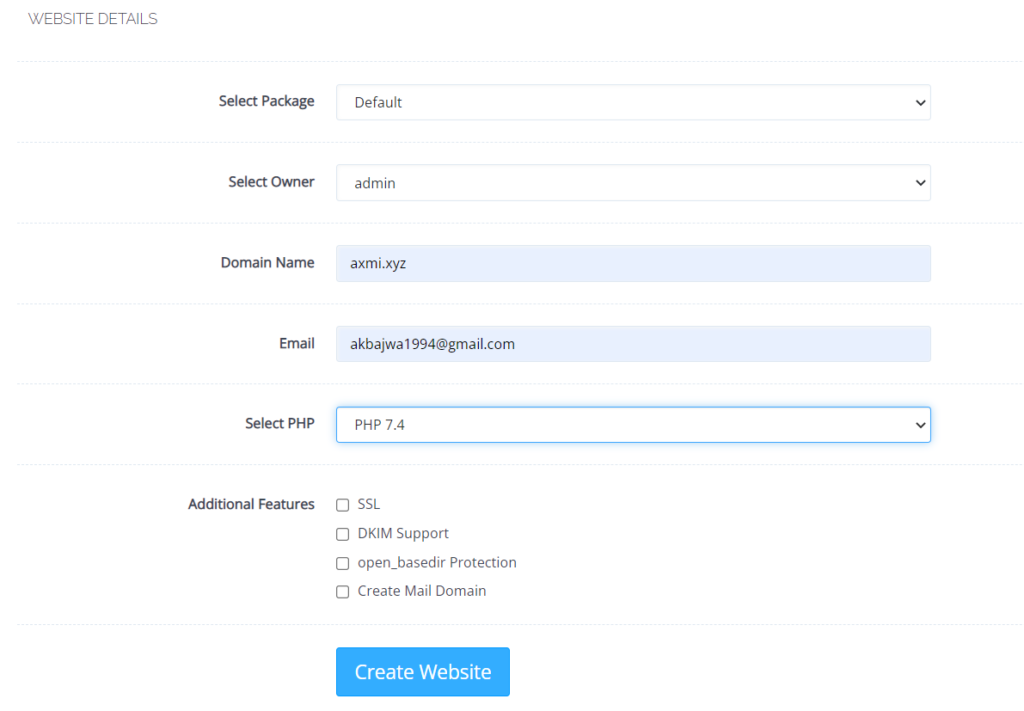
- Open your CyberPanel account dashboard and click on website -> Create Website from the left hand side menu
- Enter website details and click “Create Website”
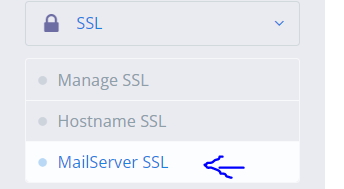
- From the left hand side menu, click SSL -> MailServer SSL
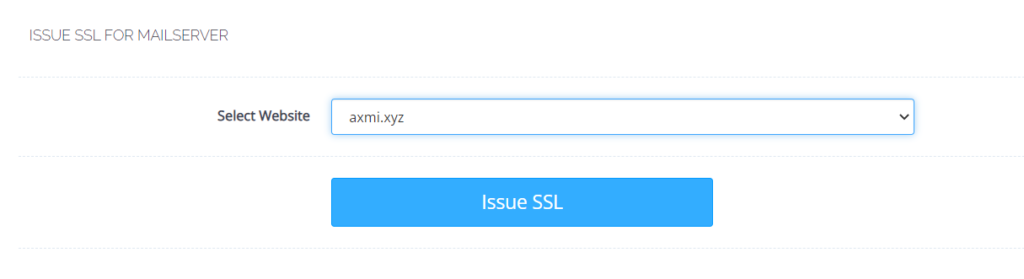
- Select your domain and click “Issue SSL”
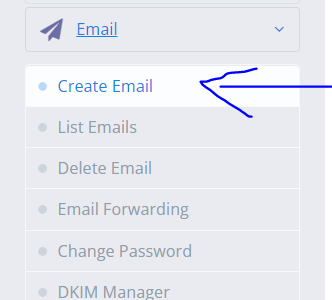
Create Email in CyberPanel
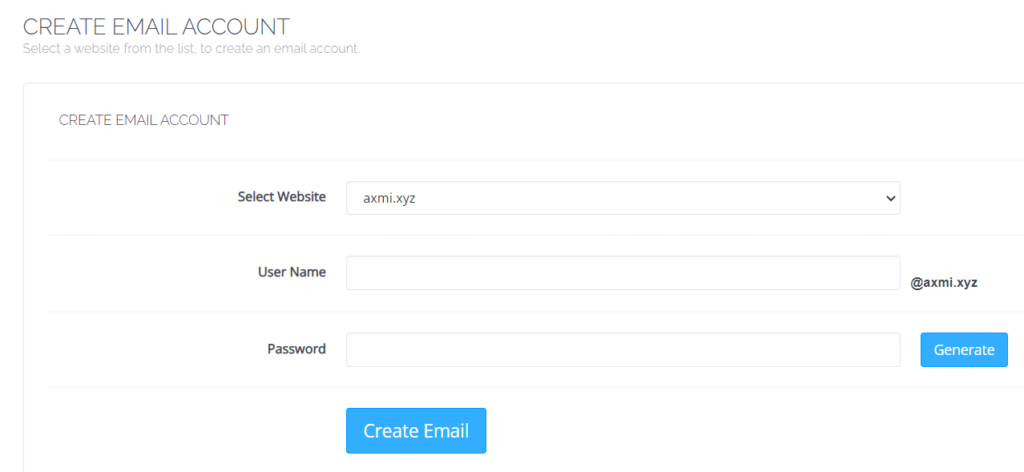
- Open “Create Email” from the left hand side menu
- Enter your email account credentials and click “Create Email”
Edit postfix Configuration file
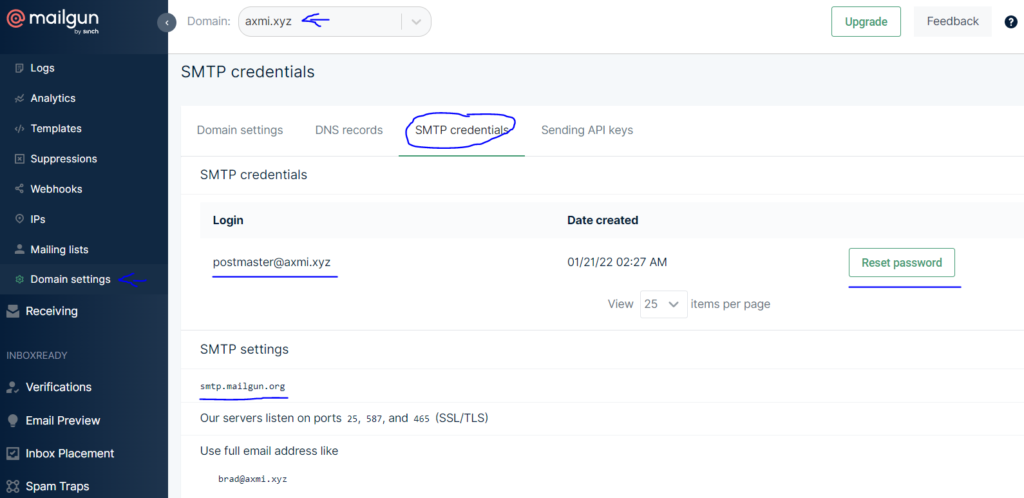
- In Mailgun, open “Domain settings” from the left hand side menu and select your domain and click SMTP credentials. Here you will get your host, login user and password. Click on reset password to get your password simply copy it and save it.
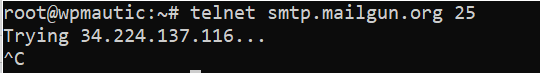
- First we need to see whether or not our port 25 is blocked or not, because if port 25 is blocked we will use port 587. Login to your server ‘s SSH and open terminal. Enter the
telnetcommand with host and port 25 to check whether it is open.
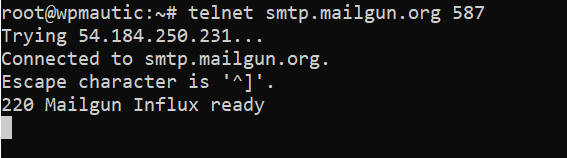
- As you can see above that port 25 seems blocked learn more about that here , try
telnetwith 587 (DNS SSL Port), as you can see port 587 is opened, we will use this port in our configurations
- Enter
quitcommand
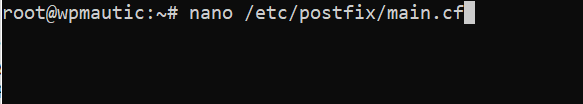
- Use nano to open the Postfix configuration file /etc/postfix/main.cf
- Hold the down button, to come to the very bottom of the file and post the following
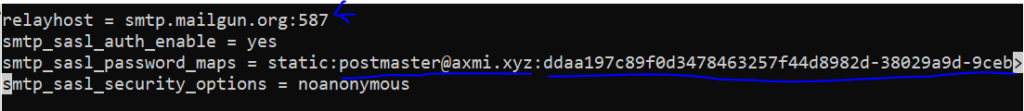
relayhost = <Mailgun_host>:587
Change <Mailgun_host> with actual Mailgun host from your account, change <Mailgun_user> with actual Mailgun smtp user and change <Mailgun_password> with actual SMTP password from your Mailgun account.
smtp_sasl_auth_enable = yes
smtp_sasl_password_maps = static:<Mailgun_user>:<Mailgun_password>
smtp_sasl_security_options = noanonymous
Our configuration file looked like this:
- Click Ctrl + O to write out and click enter
- Click Ctrl + X to exit the file
Once configurations are saved don’t forget to restart postfix using systemctl restart postfix
Send test email
- Now open your CyberPanel account and click Email -> Access Webmail
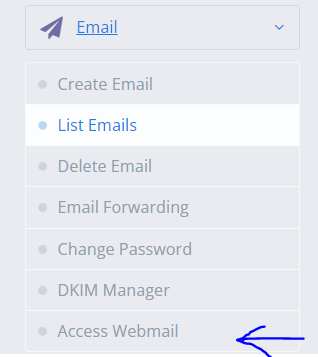
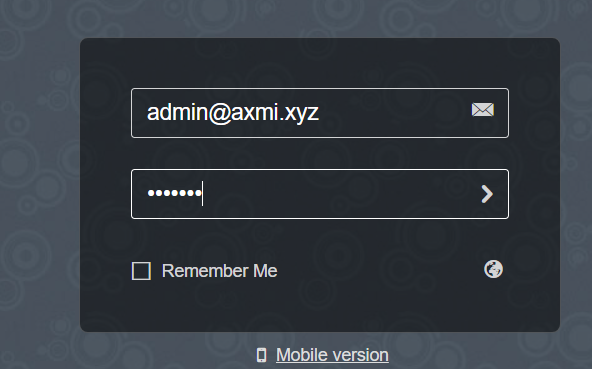
- Enter your user email and password (user and password for email account that you have created above) and click enter
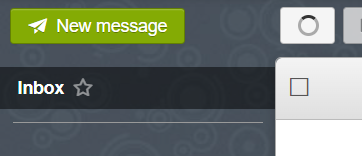
- From the upper right corner, click “New Message”
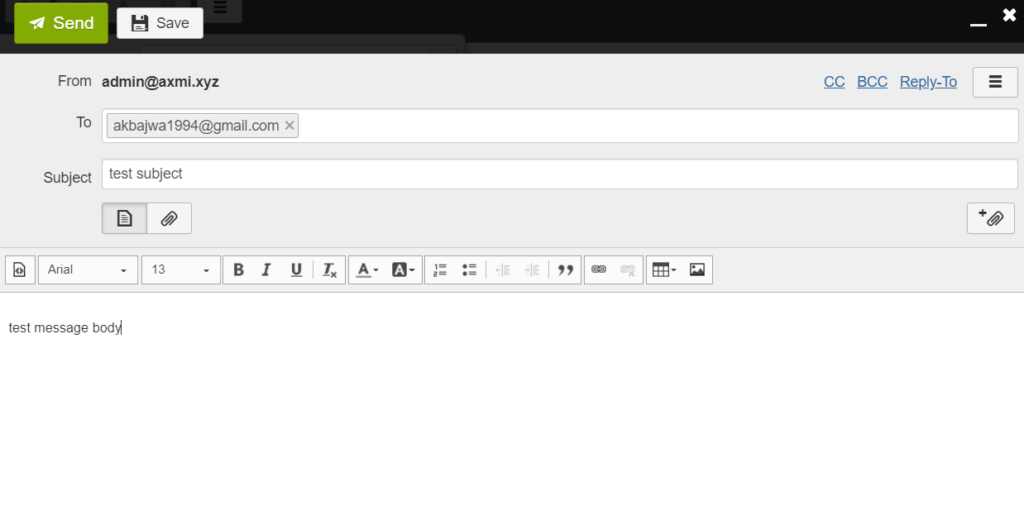
- Create a test email and click send
Check your logs in Mailgun
Go in Mailgun and click “Logs” from the left hand side menu. Select your domain. You will see your sent email log over here
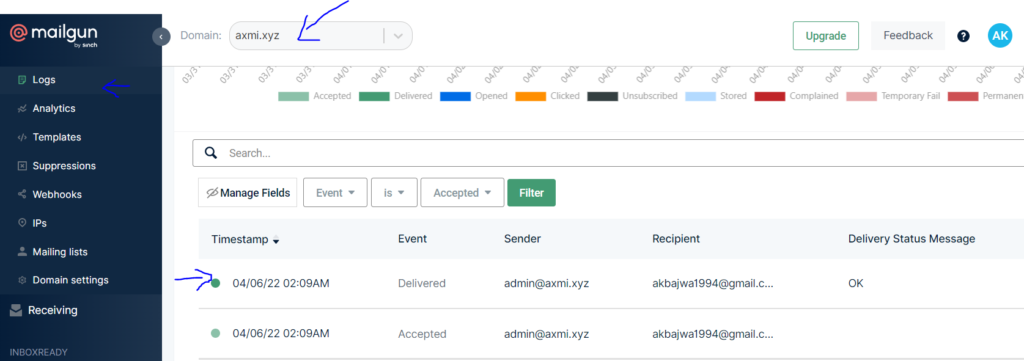
- You have successfully setup a Mailgun SMTP relay
Conclusion
The simplest method to get started sending emails is to use an SMTP relay provider. Set up your SMTP server after adding and verifying your domain name and choosing between a dedicated or shared IP address. Your username, password, SMTP server host name, and SMTP port are the only four pieces of information you’ll need. After you’ve entered them into your application’s SMTP configuration settings, you’re ready to use Mailgun to send outgoing mail. To enhance security to your email, you can utilize a normal or SSL connection depending on the port you select.